Abstract
Augmented Reality (AR) today has become one of the most exponentially growing technology. Right from its development, it has been in huge demand for various reasons; be it entertainment purpose, scientific and technological reason etc. Its unique capability of modifying the real world and giving it a new picture with the use of different media has been winning millions of hearts. To explain Augmented Reality in simple terms, we can take the example of the game “Pokemon Go” which gained a large popularity due to its interesting feature of letting you see and catch the Pokemon in front of you. This gives the clear idea of how Augmented Reality works.
Introduction
Augmented Reality is a technology that makes a real-world more dynamic by adding digital data onto it. Simply putting change of perception towards your real environment by superimposing it with computer-generated graphics, sounds, texts or any other digital information. An important thing to know is that unlike Virtual Reality (VR) AR does not create a virtual environment as a whole but adds virtual objects to your real world. Another best example to understand AR is the Snapchat app that wonderfully adds a dog’s ears or heart eyes to a person’s face. You may seldom realise the AR principle behind the apps that you use or games that you play but it’s alright. It wouldn’t be wrong to say that AR has been successful in making people amazed of its outstanding features.

Fig 1.0 Look of Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality is defined as the technology and methods that allow overlaying of real-world objects and environments with 3D virtual objects using an AR device, and allow the virtual to interact with the real-world objects to create intended meanings. Augmented Reality has moved beyond headsets and gaming and permeated into numerous industries. In general terms, Augmented Reality is increasingly being adopted for a variety of uses like assembly, maintenance, repair, education, training, retail showcasing, and diagnostics.
1) What are the real-world applications of Augmented Reality?
DEFENCE
It helps in improving the situational awareness of the soldiers using AR technology. The tech is named as Tactical Augmented Reality (TAR). This tech has an eyepiece that assists soldiers on the battlefield to precisely locate their positions in addition to the location of others (friends and enemy soldiers). Impact of this technology in Defence
- TAR will one day replace night vision goggles, as this technology can help soldiers in the dark.
- It will replace the handheld GPS that soldiers carry today to locate their positions.
- The eyepiece is wirelessly connected to a thermal site on the soldiers’ rifle or carbine.When the soldier is pointing the weapon, the image of the target, plus other details, such as the distance to the target can be seen through the eyepiece.
HEALTHCARE
Traditionally handheld ultrasound scanners are used in reconstruction surgery for locating blood vessels, and bones. However, AR technology has the potential to replace ultrasound scanners as it will help in locating the blood vessels very accurately and in a shorter period.
PHARMACEUTICALS
Augmented Reality tools can help scientists to picture the structure of complex molecules. Drug developers usually work with static models. The AR will help the developers to step inside the molecule and see how it moves and responds to different stimuli and situations. This will reduce errors and reduce the years-long drug development cycle.
LOGISTICS
AR will benefit logistics industries at multiple levels of their operations.
- Optimizing warehouse operations
- Optimizing transportation
- Last-mile delivery
- Enhanced value-added services
2) How Augmented Reality is different from Virtual Reality and Mixed Reality?
Augmented Reality
Integrates text, graphics, audio, and adds value to the users’ interaction with the real world as Transparent screen.
AR does not replace actual world environment with 3D digital elements.
AR combines both the real-world and the virtual. Users of AR are still able to sense the real world around them.
Virtual Reality
Simulation of Reality on Opaque screen.
VR replaces the actual world environment with 3D digital elements.
VR is a completely computer-generated three-dimensional environment that is displayed either on a computer screen or through special displays.
Mixed Reality
- It is a combination of AR and VR; allows a person to see and immerse oneself in the real world while simultaneously interacting with the virtual environment using hands.
Augmented reality continues to develop and become more pervasive among a wide range of applications. Since its conception, marketers and technology firms have had to battle the perception that augmented reality is little more than a marketing tool. However, there is evidence that consumers are beginning to derive tangible benefits from this technology and expect it as part of their purchasing process. Some experts have long speculated that wearable devices could be a breakthrough for augmented reality. Smartphones and tablets show a tiny portion of the user’s landscape, but smart eyewear, for example, may provide a more complete link between real and virtual realms if it develops enough to become mainstream.

Fig 1.1 AR VR
Any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic.
One such magic of advanced technology is Augmented reality.
3) Types Of AR
Augmented reality is of four types: Marker-less, Marker-based, Projection-based, and Superimposition-based AR. Let us see them one by one in detail.
a) Marker-based AR
A marker, which is a special visual object like a special sign or anything, and a camera are used to initiate the 3D digital animations. The system will calculate the orientation and position of the market to position the content effectively.
Marker-based AR example: A marker-based mobile-based AR furnishing app.
b) Marker-less AR
It is used in events, business, and navigation apps, for instance, the technology uses location-based information to determine what content the user gets or finds in a certain area. It may use GPS, compasses, gyroscopes, and accelerometers as can be used on mobile phones.
c) Project-based AR
This kind uses synthetic light projected on the physical surfaces to detect the interaction of the user with the surfaces. It is used on holograms like in Star Wars and other sci-fi movies.
d) Superimposition-based AR
In this case, the original item is replaced with an augmentation, fully or partially. The below example is allowing users to place a virtual furniture item over a room image with a scale on the IKEA Catalog app.
IKEA is an example of superimposition-based AR
4) How Does AR Work: Technology Behind It
First is the generation of images of real-world environments. Second is using technology that allows the overlaying of 3D images over the images of the real-world objects. The third is the use of technology to allow users to interact and engage with the simulated environments. AR can be displayed on screens, glasses, handheld devices, mobile phones, and head-mounted displays. As such, we have mobile-based AR, head-mounted gear AR, smart glasses AR, and web-based AR. Headsets are more immersive than mobile-based and other types. Smart glasses are wearable AR devices that provide first-person views, while web-based do not require downloading of any app.
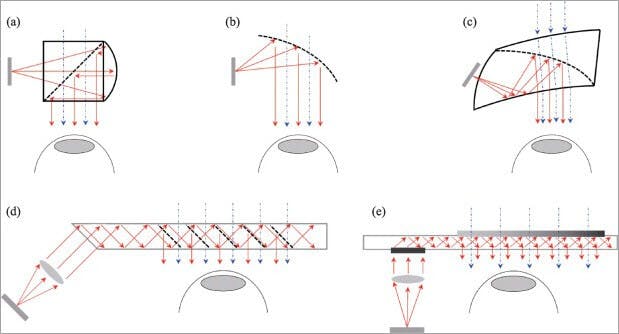
Fig 1.2 Configuration of AR Glasses
It uses S.L.A.M. technology (Simultaneous Localization And Mapping), and Depth Tracking technology for calculating the distance to the object using sensor data, in addition to other technologies.
5) Augmented Reality Technology
AR technology allows real-time augmentation and this augmentation takes place within the context of the environment. Animations, images, videos, and 3D models may be used and users can see objects in natural and synthetic light. In AR, SLAM helps slot and blend the virtual object into a real object.
Recognition-based AR: It is a camera to identify markers so that an overlay is possible if there is a marker detected. The device detects and calculates the position and orientation of the marker and replaces the real world marker with its 3D version. Then it calculates the position and orientation of others. Rotating the marker rotates the entire object.
Location-based Approach: Here the simulations or visualizations are generated from data collected by GPS, digital compasses, accelerometers, and velocity meters. It is very common in smartphones.
Depth tracking technology: Depth map tracking cameras such as Microsoft Kinect generate a real-time depth map by using different technologies to calculate the real-time distance of objects in the tracking area from the camera. The technologies isolate an object from the general depth map and analyse it.
Natural feature tracking technology: It may be used to track rigid objects in a maintenance or assembly job. A multistage tracking algorithm is used to estimate the motion of an object more accurately. Marker tracking is used, as an alternative, alongside calibration techniques. The overlaying of virtual 3D objects and animations on real-world objects is based on their geometrical relationship. Extended face-tracking cameras are now available on smartphones such as iPhone XR which has TrueDepth cameras to allow better AR experiences.
6) Components of AR
For AR a certain range of data (images, animations, videos, 3D models) may be used and people will see the result in both natural and synthetic light. Also, users are aware of being in the real world which is advanced by computer vision, unlike in VR.
AR can be displayed on various devices: screens, glasses, handheld devices, mobile phones, head-mounted displays. It involves technologies like S.L.A.M. (simultaneous localization and mapping), depth tracking (briefly, a sensor data calculating the distance to the objects), and the following components:
Cameras and sensors Collecting data about user’s interactions and sending it for processing. Cameras on devices are scanning the surroundings and with this info, a device locates physical objects and generates 3D models. It may be special duty cameras, like in Microsoft Hololens, or common smartphone cameras to take pictures/videos.
Processing AR devices eventually should act like little computers, something modern smartphones already do. In the same manner, they require a CPU, a GPU, flash memory, RAM, Bluetooth/WiFi, a GPS, etc. to be able to measure speed, angle, direction, orientation in space, and so on.
Projection This refers to a miniature projector on AR headsets, which takes data from sensors and projects digital content (result of processing) onto a surface to view. In fact, the use of projections in AR has not been fully invented yet to use it in commercial products or services.
Reflection Some AR devices have mirrors to assist human eyes to view virtual images. Some have an “array of small curved mirrors” and some have a double-sided mirror to reflect light to a camera and to a user’s eye. The goal of such reflection paths is to perform a proper image alignment.
7) Developing And Designing For AR
AR development platforms are platforms on which you can develop or code AR apps. Examples include ZapWorks, ARToolKit, MAXST for Windows AR and smartphone AR, DAQRI, SmartReality, ARCore by Google, Windows’ Mixed Reality AR platform, Vuforia, and ARKit by Apple. Some allow the development of apps for mobile, others for P.C., and on different operating systems.
AR development platforms allow developers to give apps different features such as support for other platforms such as Unity, 3D tracking, text recognition, creation of 3D maps, cloud storage, support for single and 3D cameras, support for smart glasses, Different platforms allow the development of marker-based and/or location-based apps. Features to consider when selecting a platform include cost, platform support, image recognition support, 3D recognition, and tracking is a most important feature, support for third-party platforms such as Unity from where users can import and export AR projects and integrate with other platforms, cloud or local storage support, GPS support, SLAM support, etc.
The AR apps developed with these platforms support a myriad of features and capabilities. They may allow content to be viewed with one or a range of AR glasses that have pre-made AR objects, support for reflection mapping where objects have reflections, real-time image tracking, 2D and 3D recognition.
Some SDK or software development kits allow the development of apps by drag and drop method while others require knowledge in coding. Some AR apps allow users to develop from scratch, upload, and edit, own AR content.
8) AR Example In Real Life
Elements 4D is a chemistry learning application that employs AR to make chemistry more fun and engaging. With it, students make paper cubes from the element blocks and place them in front of their AR cameras on their devices. They can then see representations of their chemical elements, names, and atomic weights. Students can bring together the cubes to see if they react and to see chemical reactions.
Google Expeditions, where Google uses cardboards, already allows the students from across the world to do virtual tours for history, religion, and geography studies.
Human Anatomy Atlas lets students explore over 10,000 3D human body models in seven languages, to let students learn the parts, how they work, and to improve their knowledge.
Touch Surgery simulates surgery practice. In partnership with DAQRI, an AR company, medical institutions can see their students practicing surgery on virtual patients.
Fig 1.3 AR used in Surgery.
- IKEA Mobile App is famous in real estate and home product walkthroughs and testing. Other apps include Nintendo’s Pokemon Go App for gaming.
This Ingenious Augmented Reality mirror will take telepresence to a new level.
9) Augmented reality devices
Many modern devices already support Augmented reality. From smartphones and tablets to gadgets like Google Glass or handheld devices, and these technologies continue to evolve. For processing and projection, AR devices and hardware, first of all, have requirements such as sensors, cameras, accelerometer, gyroscope, digital compass, GPS, CPU, displays, and things we’ve already mentioned. Devices suitable for Augmented reality fall into the following categories:
Mobile devices (smartphones and tablets) – the most available and best fit for AR mobile apps, ranging from pure gaming and entertainment to business analytics, sports, and social networking.
Special AR devices, designed primarily and solely for augmented reality experiences. One example is head-up displays (HUD), sending data to a transparent display directly into user’s view. Originally introduced to train military fighters pilots, now such devices have applications in aviation, automotive industry, manufacturing, sports, etc.
AR glasses (or smart glasses) – Google Glasses, Meta 2 Glasses, Laster See-Thru, Laforge AR eyewear, etc. These units are capable of displaying notifications from your smartphone, assisting assembly line workers, access content hands-free, etc.
AR contact lenses (or smart lenses), taking Augmented Reality one step even farther. Manufacturers like Samsung and Sony have announced the development of AR lenses. Respectively, Samsung is working on lenses as the accessory to smartphones, while Sony is designing lenses as separate AR devices (with features like taking photos or storing data).
Virtual retinal displays (VRD), creating images by projecting laser light into the human eye. Aiming at bright, high contrast and high-resolution images, such systems yet remain to be made for a practical use.
AR in retail may act to bring better customer engagement and retention, as well as brand awareness and more sales. Some features may also help customers make wiser purchases – providing product data with 3D models of any size or color. Real-estate can also benefit from Augmented Reality via 3D tours of apartments and houses, that can also be manipulated to amend some parts. Other potential areas for AR include:
Education: interactive models for learning and training purposes, from mathematics to chemistry.
Medicine/healthcare: to help diagnose, monitor, train, localize, etc.
Military: for advanced navigation, marking objects in real time.
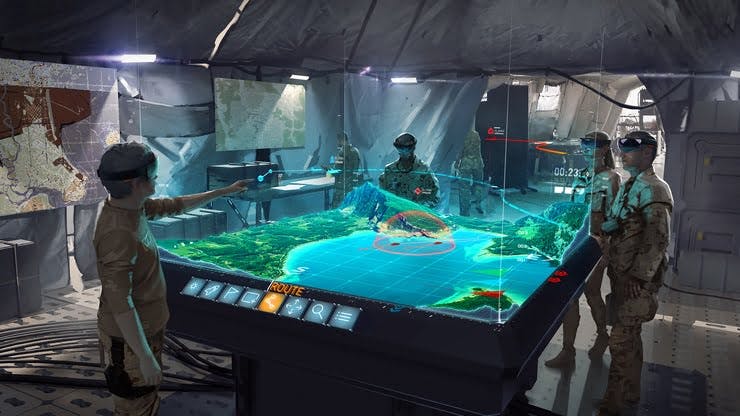

Fig 1.4 AR in Military
Art / installations / visual arts / music.
Tourism: data on destinations, sightseeing objects, navigation, and directions.
Broadcasting: enhancing live events and event streaming by overlaying content.
Industrial design: to visualize, calculate or model.
10) The future of augmented reality
With the release of iOS 11 and its ARKit in 2017, augmented reality became even closer to a common smartphone user. ARCore from Google made augmented reality available for Android users as well.
The projected growth of this market is impressive, projected to reach $97.76bn by 2028. While it is difficult to make any predictions, as nobody knows for sure how the augmented reality will look like in five or ten years, the potential it shows now is great, and big tech companies seem to believe that this technology will stay and evolve in the future. Facebook, Apple, Google and other tech giants are releasing and improving their AR kits to make the development easier and cheaper. AR can indeed become a great tool for any industry.
The massive success of Pokemon Go proved it to be true — it’s probably the first thing that comes to mind when we think about augmented reality.
Unlike virtual reality that creates a fully virtual environment around a user, augmented reality integrates virtual objects into existing surroundings. This makes it more interactive and real.
Another great thing about AR is that you only need your smartphone to enjoy it — you won’t need bulky and expensive VR headsets. This means, that AR has greater chances to become more widespread. That’s why many startups are looking towards using augmented reality for business.
11) Augmented Reality Applications
Gaming: AR allows for better gaming experiences as gaming grounds are being moved from virtual spheres to include real-life experiences where players can perform real-life activities to play.
Retail and Advertisement: AR can improve customer experiences by presenting customers with 3D models of products and helping them make better choices by giving them virtual walkthroughs of products such as in a real estate. It can be used to lead customers to virtual stores and rooms. Customers can overlay the 3D items on their spaces such as when buying furniture to select items best suitable to match their spaces – regarding size, shape, color, and type. In advertising, ads can be included in AR content to help companies popularize their content to viewers.
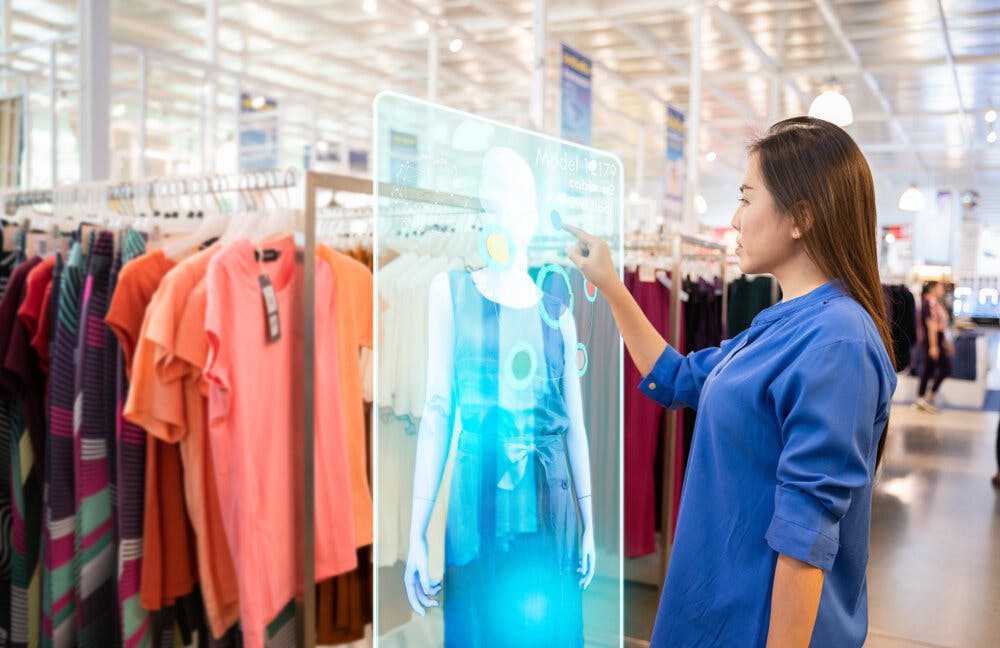

Fig 1.5 Augmented Reality in Real Life
Manufacturing and Maintenance: In maintenance, repair technicians can be directed remotely by professionals to do repairs and maintenance works while on the ground using AR apps without having the professionals travel on the location. This can be useful in places where it is hard to travel to the location.
Education: AR interactive models are used for training and learning.
Military: AR assists in advanced navigation and to help mark objects in real-time.
Tourism: AR, in addition to placing ads on AR content, can be used for navigation, providing data on destinations, directions, and sightseeing.
Medicine/Healthcare: AR can help train healthcare workers remotely, help in monitoring health situations, and for diagnosing patients.
12) Benefits Of AR
Let us see some benefits of AR for your business or organization and how to integrate it:
Integration or adoption depends on your use case and application. You may want to employ it for monitoring maintenance and production work, perform virtual walkthroughs of real estate property, advertise products, boost remote design, etc.
Today, virtual fitting rooms can help decrease purchase returns and improve purchase decisions made by buyers.
Salespeople can produce and publish interesting branded AR content and insert ads in them so people can get to know their products when they watch the content. AR improves engagement.
In manufacturing, AR markers on images of manufacturing equipment help project managers to monitor work remotely. It reduces the need to use digital maps and plants. For instance, a device or machine can be pointed on location to determine if it will fit on position.
Immersive real-life simulations are delivering pedagogical benefits to learners. Simulations in game-based learning and training come in with psychological benefits and increase empathy among learners as shown by researchers.
Medical students can use AR and VR simulations to try first and as many surgeries as possible without hefty budgets or unnecessary injuries to patients, all with immersion and near-real experiences.
Using AR, future astronauts can try their first or next space mission.
AR enables virtual tourism. AR apps, for instance, can provide directions to desirable destinations, translate the signs on the street, and provide information on sight-seeing. A good example is a GPS navigation app. AR content enables the production of new cultural experiences, for instance, where additional reality is added to museums.
Augmented reality is expected to expand to $150 billion by 2020. It is expanding more than virtual reality with $120 billion compared to $30 billion. AR-enabled devices are expected to reach 2.5 billion by 2023.
Developing own branded applications is one of the most common ways that the companies are using to engage with AR technology. Companies can still place ads on third-party AR platforms and content, buy licenses on developed software, or rent spaces for their AR content and audiences.
Developers can use AR development platforms such as ARKit and ARCore to develop applications and integrate AR into business applications.
13) Drawbacks or disadvantages of Augmented Reality (AR)
Following are the drawbacks or disadvantages of Augmented Reality (AR):
It is expensive to develop the AR based projects and also difficult to maintain it. Moreover, production of AR based devices is costly.
Lack of privacy in AR based applications.
Low performance level is a concern which needs to be addressed during testing process.
It requires basic learning to effectively use AR compliant devices.
Conclusion
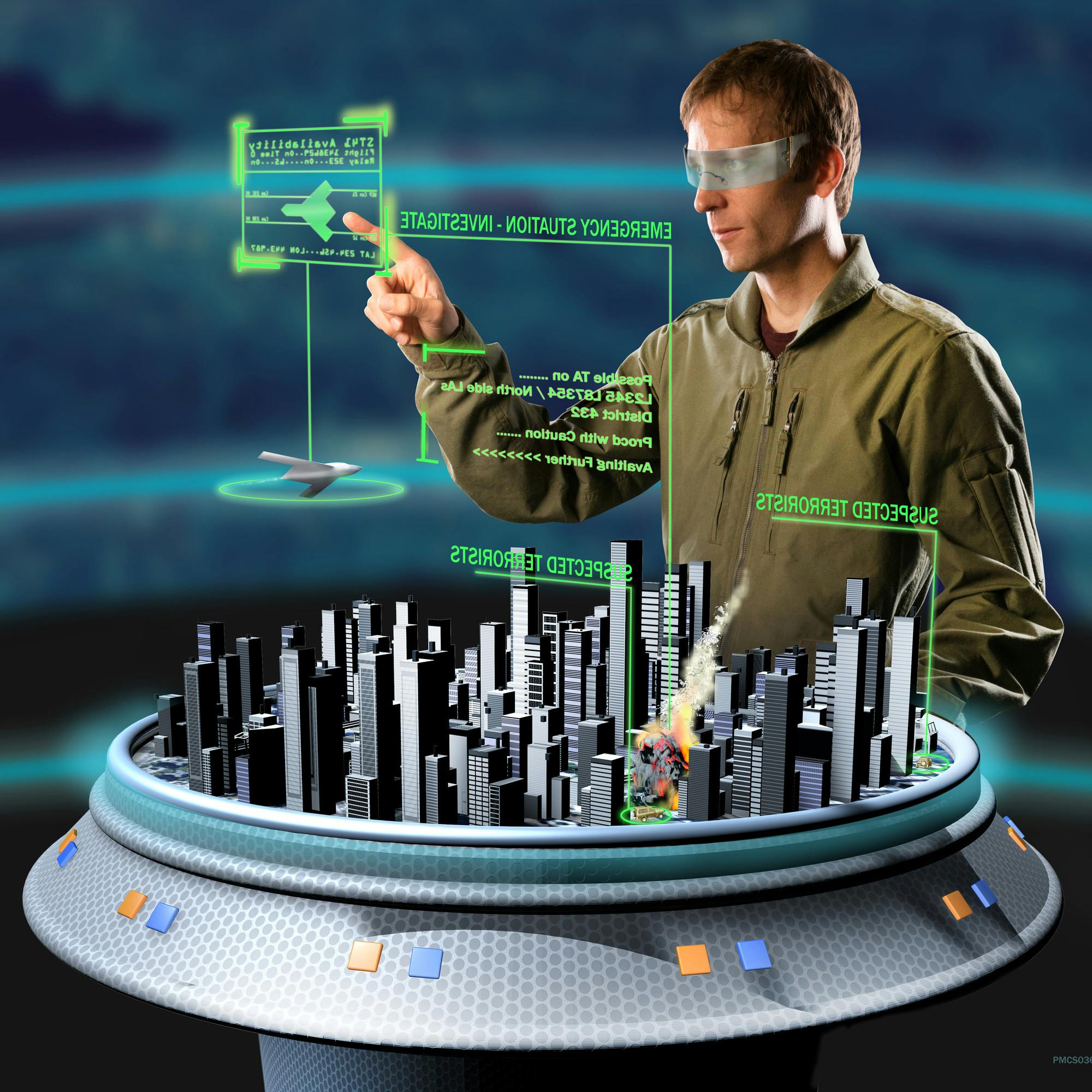

Fig 1.6 Augmented Reality - A tool of future.
Augmented Reality allows the overlaying of virtual objects in real-world environments. It uses a combination of technologies including SLAM, depth tracking, and natural feature tracking, and object recognition, among others.
Augmented Reality
Interactive worlds you can hold in the palm of your hand.
